Homeostasis in Human, Animals, and Plants
1. Which organ is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the human body?
a) Liver
b) Kidneys
c) Heart
d) Lungs
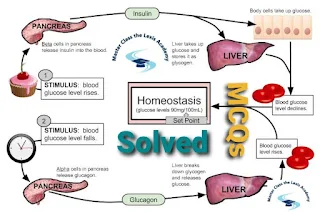
2. Which hormone regulates blood sugar levels and plays a key role in glucose homeostasis?
a) Insulin
b) Thyroxine
c) Cortisol
d) Glucagon
3. During exercise, which physiological response helps regulate body temperature and prevent overheating?
a) Increased heart rate
b) Sweating
c) Constriction of blood vesselsLqqll
d) Slowed respiratory rate
4. What is the function of the hypothalamus in the context of homeostasis?
a) Regulation of sleep
b) Control of body temperature
c) Production of digestive enzymes
d) Maintenance of muscle tone
5. Which of the following is NOT a component of the feedback loop in homeostasis?
a) Receptor
b) Effector
c) Stimulus
d) Initiator
6. How does the respiratory system contribute to maintaining acid-base balance in the body?
a) Excreting excess acids through urine
b) Releasing bicarbonate ions into the blood
c) Producing ammonia to neutralize acids
d) Constricting blood vessels
7. What role do red blood cells play in homeostasis?
a) Oxygen transport
b) Digestion
c) Hormone production
d) Waste elimination
8. Which electrolyte is essential for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction in the human body?
a) Sodium
b) Potassium
c) Calcium
d) Magnesium
9. In response to low blood oxygen levels, which physiological adaptation occurs to increase oxygen delivery to tissues?
a) Increased heart rate
b) Vasodilation
c) Formation of blood clots
d) Constriction of airways
10. What is the purpose of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in maintaining blood pressure and fluid balance?
a) Regulation of glucose levels
b) Promotion of water excretion
c) Conservation of sodium and water
d) Control of body temperature
11. What is the primary purpose of homeostasis in plants?
a) Reproduction
b) Growth
c) Maintenance of internal stability
d) Photosynthesis
12. Which plant hormone is responsible for promoting cell elongation and regulating plant growth?
a) Abscisic acid
b) Gibberellins
c) Ethylene
d) Auxins
13. How do plants regulate water balance to maintain homeostasis?
a) Transpiration and guttation
b) Photosynthesis and respiration
c) Absorption and assimilation
d) Germination and dormancy
14. What is the role of stomata in the context of plant homeostasis?
a) Nutrient absorption
b) Gases exchange
c) Flower development
d) Water storage
15. Which environmental factor does NOT influence plant homeostasis?
a) Light intensity
b) Temperature
c) Atmospheric pressure
d) Sound waves
16. What is homeostasis?
a) The study of animal behavior
b) The maintenance of a stable internal environment
c) The process of reproduction in animals
d) None of the above
17. Which organ plays a crucial role in regulating blood glucose levels?
a) Liver
b) Kidneys
c) Lungs
d) Stomach
18. How do animals regulate body temperature in a cold environment?
a) Sweating
b) Vasodilation
c) Shivering
d) Vasoconstriction
19. Which hormone is responsible for water reabsorption in the kidneys?
a) Insulin
b) Estrogen
c) Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
d) Cortisol
20. What is the primary function of negative feedback in homeostasis?
a) Amplify deviations from the set point
b) Maintain stability by counteracting deviations
c) Shut down the entire system
d) None of the above
21. What is the primary function of the urinary system in humans?
a. Digestion
b. Respiration
c. Excretion
d. Circulation
22. Which organ in the urinary system filters blood and produces urine?
a. Liver
b. Kidneys
c. Bladder
d. Pancreas
23. What is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for filtering blood and forming urine?
a. Nephron
b. Alveoli
c. Neuron
d. Bronchus
24. Which of the following substances is NOT typically found in normal urine?
a. Urea
b. Glucose
c. Sodium
d. Creatinine
25. The tube connecting the kidney to the bladder is called:
a. Urethra
b. Ureter
c. Trachea
d. Esophagus
26. Where is urine stored before it is eliminated from the body?
a. Kidney
b. Ureter
c. Bladder
d. Urethra
27. Which condition is characterized by the presence of kidney stones?
a. Nephritis
b. Glomerulonephritis
c. Nephrolithiasis
d. Pyelonephritis
28. The process of expelling urine from the body is known as:
a. Filtration
b. Micturition
c. Secretion
d. Absorption
29. What is the primary function of the kidneys in the human body?
a. Digestion
b. Filtration of blood
c. Respiratory exchange
d. Muscle contraction
30. Which is the functional unit of the kidney that regulates electrolyte balance and blood pressure?
a. Glomerulus
b. Loop of Henle
c. Bowman's capsule
d. Renal tubule
31. Which hormone is produced by the kidneys to stimulate red blood cell production in the bone marrow?
a. Insulin
b. Estrogen
c. Erythropoietin
d. Thyroxine
32. What is the normal pH range of urine in a healthy individual?
a. 5.0 - 6.0
b. 6.5 - 7.5
c. 7.0 - 8.0
d. 8.5 - 9.5
33. Which blood vessel supplies blood to the kidneys for filtration?
a. Renal artery
b. Pulmonary vein
c. Coronary artery
d. Hepatic portal vein
34. What is the purpose of the ureters in the urinary system?
a. Filtration of blood
b. Storage of urine
c. Transport of urine to the bladder
d. Absorption of water
35. Which part of the nephron reabsorbs water and electrolytes back into the bloodstream?
a. Glomerulus
b. Loop of Henle
c. Distal tubule
d. Proximal tubule
36. Which condition results from the accumulation of waste products in the blood due to kidney failure?
a. Diabetes
b. Hypertension
c. Anemia
d. Uremia
37. Which of the following is a common symptom of kidney stones?
a. Hypertension
b. Hematuria (blood in urine)
c. Hyperglycemia
d. Respiratory distress
41. Where does filtration of blood occur in the nephron?
a. Proximal convoluted tubule
b. Distal convoluted tubule
c. Loop of Henle
d. Glomerulus
42. What is the main function of the collecting duct in the nephron?
a. Filtration
b. Reabsorption
c. Secretion
d. Concentration of urine
43. What is the purpose of the renal pelvis in the kidney?
a) Filtration
b) Reabsorption
c) Storage of urine
d) Secretion of hormones
44. Which blood vessels supply the kidneys with oxygenated blood?
a) Renal arteries
b) Pulmonary veins
c) Coronary arteries
d) Aorta
45. What is the term for the process of removing waste products from the blood in the kidneys?
a) Dialysis
b) Osmosis
c) Filtration
d) Absorption
46. Which substance is typically reabsorbed in the renal tubules to maintain body balance?
a) Glucose
b) Urea
c) Sodium
d) Creatinine
47. What condition is characterized by the inflammation of the kidneys?
a) Nephritis
b) Cirrhosis
c) Appendicitis
d) Arthritis
48Which of the following is NOT a function of the kidneys?
a) Regulation of blood pressure
b) Production of red blood cells
c) Conversion of glucose to glycogen
d) Acid-base balance
49. Where do the Red Blood Cells are formed?
a. Liver
b. Heart
c. Bone Marrow
d. Pancreas
50. Where does protein get digested?
a. Kidneys
b. Pancreas
c. Small Intestine
d. Stomach
Also Read the Following Suggested Topics for Further Reading
Enzymes in Biology Solved MCQs
Vitamins in Biology Solved MCQs
Laws of Inheritance in Biology Solved MCQs
Nutrition in Plants Solved MCQs
Bioenergetics in Plants Solved MCQs
Respiration in Plants and AnimalsSolved MCQs
Reproduction in Plants and Animals Solved MCQs
Animal and Plant Cell Solved MCQs
Biology in General Solved MCQs
Comments